Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine, in which degenerative processes occur in the cartilage and joints. It is characterized by the thinning of the intervertebral discs and a decrease in their elasticity.
Characteristics of the disease.
This disease mainly affects the elderly. Although scientists point out that the manifestations of the disease begin more and more often from the age of thirty, or even earlier. This suggests that the disease has gotten much younger.

The intervertebral discs provide a shock absorption function, but in case of illness, they cannot cope with their task. A person suffering from osteochondrosis almost always complains of pain, while pain can manifest itself locally and remotely. A person feels stiff in movements, lethargy and fatigue.
Basically, the pain manifests itself in the section affected by the disease.
Location of pathology and its types.
Depending on which part of the spine is damaged by pathology, 4 types of osteochondrosis are distinguished:
- Cervical osteochondrosis. . . It occurs in the case of pathological changes in the cervical spine. The vertebrae become brittle, the load on the cervical spine increases, which can lead to disruption of the thyroid gland, pinching the artery that supplies blood to the brain.
- Thoracic osteochondrosis. . . Pathological changes occur in the thoracic spine. It is diagnosed in patients less often than other types, since the thoracic vertebrae are less mobile and are protected by stronger muscles. Symptoms of this type are similar to those of cardiovascular disease.
- Lumbar osteochondrosis. . . This type is the most common. Since the lumbar spine has the greatest load.
- Set. . . It occurs in the case of damage to several parts of the spine at once.
Along with this, the disease can affect other joints. Most of the time they suffer:
- Shoulder joint. . . As a rule, the disease is caused by the transition from osteochondrosis of the cervical spine to the shoulder joint.
- Hip joint. . . It occurs due to changes in cartilage tissue and a lack of fluid between the joints.
- Knee joint. . . Chondrosis can manifest itself in 3 ways:
- Koenig's disease, in which cartilage tissue is affected.
- Larsen-Johansson disease, in which changes occur in the joint above the knee.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease, related to changes in the tibia.
Classification and degree of manifestation of the disease.
The disease can be classified according to the degree of manifestation. At the same time, it is difficult to determine the degree of the disease before the appearance of the characteristic pains. There are 4 degrees of manifestation of the disease:
- The initial stage of the development of the disease. It occurs due to the displacement of the spinal disc associated with careless weight lifting. It is characterized by unstable pain sensations. At this stage, the disease is difficult to diagnose, but it can be easily treated.
- This stage is characterized by gradual destruction of the intervertebral disc, desiccation, and loss of shock absorbing properties. This leads to increased stress on blood vessels and nerve endings. Pain sensations intensify and are more pronounced with physical exertion and sudden movements. Treatment of the disease at this stage is conservative.
- The annulus fibrosus is destroyed and an intervertebral hernia appears. There is a deformation of the spine. The pains become important. Treatment is only possible with surgery.
- In this stage, the vertebrae grow together due to the formation of osteophytes. There is a pinching of the tissues of the spine, the vertebrae lose their mobility and restrict the movement of a person. At this stage, the disease can be disabling and is no longer amenable to treatment.
Typical symptoms
Each type of disease has its own symptoms. So, for example, cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by:
- Painful sensations in arms and shoulder girdle.
- Headache.
- Dizziness and spots before the eyes.
- Instability of blood pressure.
- Loss of feeling in the fingers.
- Tinnitus
For pathology of the thoracic region, the symptoms are characteristic:
- Pain in the region of the heart.
- Painful sensations in hypochondria.
- Shortness of breath due to sharp pains of a stabbing nature.
When the disease is localized in the lumbar spine, there are:
- Painful sensations in the lower back.
- Decreased sensation in the legs.
- Radiating pain in the legs.
- Violation of the pelvic organs.
There are also general symptoms that do not depend on the location of the disease:
- Back pain.
- Muscle spasms.
- Movement restriction.
- Change in pain syndrome based on load and sudden movements.
- Numbness of the extremities.
- Rapid fatigue
- Decreased sensation of the extremities.
Signs and manifestations of osteochondrosis.
The first signs of the disease begin to appear in the first stage of development. These include:
- Swelling and pain in the lower back after lying in one position for more than half an hour.
- The presence of pain in the back after a long session.
- The need to stretch after waking up and the inability to wake up and get up immediately.
- Perceived creaking in the back.
- Goose bumps and decreased sensation of the extremities.
- Unpleasant sensations in the back when bending over.
- General weakness
- Violation of reproductive function and the work of internal organs.
Also, osteochondrosis can be manifested by pain that arises when lifting weights and physical activity.
Methods for diagnosing pathology.
A complex of methods is used to diagnose osteochondrosis. It includes:
Initial examination and questioning of the patient:
- Interview a patient to clarify complaints, the duration of the onset of symptoms.
- Examination of the patient's body, study of posture, gait and movement.
- Palpation of problem areas.
- Determination of sensitivity to pain.

Instrumental diagnosis:
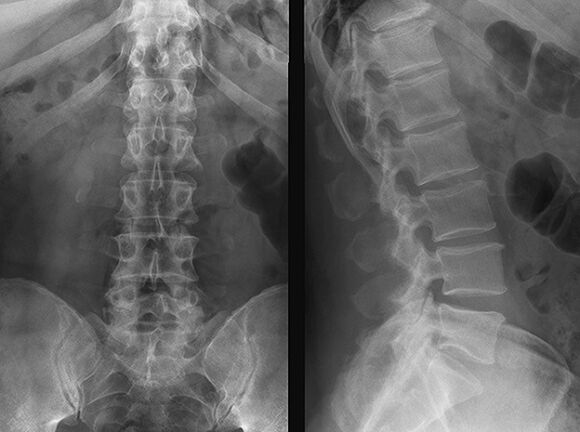
- X-ray to help identify the deformation of the intervertebral discs.
- MRI to determine the presence of a herniated disc and its location.
- Computed tomography is similar in performance to MRI, but has a higher degree of radiation.
Methods to treat the disease.
After conducting diagnostic procedures and diagnosing osteochondrosis, the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment.
Since osteochondrosis can be treated only in the early stages of development, all the main measures are aimed primarily at pain relief. To do this, apply:
- Medicine.
- Physiotherapy.
- Manual therapy.
- Massotherapy.
- Diet.
As drug treatment, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They are aimed at alleviating the inflammatory process in the area of the disease and blocking pain.
Chondroprotectors are also used to restore cartilage tissue. To maintain the normal functioning of the body, immunostimulants and vitamin complexes are used.
Physiotherapy methods are aimed at suppressing pain, normalizing metabolic processes in affected areas, improving blood circulation, relieving inflammation and edema. These include:
- Acupuncture.
- Magnetic therapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- Laser therapy.
- Paraffin therapy.
Physical therapy methods help shorten treatment times and have fewer side effects than drug treatments.
Manual therapy is a dosed effect of the doctor's hands on the affected areas of the back, to remove the restrictions that interfere with the normal functioning of the joints, muscles and ligaments.
Therapeutic massage should be performed only by a specialist and is aimed at relieving muscle tension, restoring displaced vertebrae, and normalizing blood circulation. The procedure should be done at least three times a week.
The diet for osteochondrosis aims to normalize weight, improve blood circulation, replenish collagen, eliminate calcium and mineral deficiencies, and help control fluid and salt intake. The diet must be balanced and contain many plant foods. In the fight against osteochondrosis, it is necessary to exclude such foods as: strong coffee and tea, foods rich in salt and sugar, carbonated drinks and fatty foods.
The disease, during these procedures, can be corrected and only in difficult stages requires surgical intervention.
Precautionary measures
To prevent this disease it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits, apply physical activity, use an orthopedic mattress and a pillow to sleep, avoid wearing uncomfortable shoes, it is better to wear orthopedic shoes.
You must also monitor your diet and maintain a healthy weight. With a long stay in a static state, it is necessary to allocate time for exercises that help normalize blood circulation.
Also, for the prevention and prevention of the disease, you can undergo sanatorium treatment and general strengthening massage.



























